Gulf of Guinea Contents Name Geography See also References External links Navigation menu1°0′N 4°0′E / 1.000°N 4.000°E / 1.000; 4.0001°0′N 4°0′E / 1.000°N 4.000°E / 1.000; 4.000e0°37′S 8°43′E / 0.617°S 8.717°E / -0.617; 8.7170°01′S 6°32′E / 0.017°S 6.533°E / -0.017; 6.5334°22′N 7°44′W / 4.367°N 7.733°W / 4.367; -7.733"Limits of Oceans and Seas, Draft 4th Edition: North Atlantic Ocean and its Sub-Divisions""From the Griot of Roots to the Roots of Griot: A New Look at the Origins of a Controversial African Term for Bard"The Gulf of Guinea Commission - CGG - GGCeeeege551479237228853237228853
Foxe BasinEnglish ChannelAdriatic SeaAegean SeaAlboran SeaArchipelago SeaArgentine SeaBalearic SeaBaltic SeaBlack SeaBothnian SeaCaribbean SeaCeltic SeaGreenland SeaIonian SeaIrish SeaIrminger SeaLabrador SeaLevantine SeaLibyan SeaLigurian SeaMarmara SeaMediterranean SeaMyrtoan SeaNorth SeaNorwegian SeaSargasso SeaSea of ÅlandSea of AzovSea of CreteSea of the HebridesThracian SeaTyrrhenian SeaWadden SeaAlboran SeaAtlantic OceanIndian OceanLevantine SeaMediterranean SeaRed SeaSomali SeaSouthern OceanBab-el-MandebBab IskenderCanal de BolamaCanal de BololaCanal de CaióCanal de São VicenteCanal do MeioMafia ChannelMassawa ChannelMozambique ChannelPemba ChannelShubuk ChannelGuardafui ChannelStrait of GibraltarStrait of SicilyStraits of TiranZanzibar ChannelGuinea regionGulf of GuineaCape LopezMayombeIgbolandMbaiseMaputalandPool MaleboCongo BasinChad BasinCongolese rainforestsOuaddaï highlandsEnnedi PlateauMaghrebIfriqiyaBarbary CoastBashmurAncient LibyaAtlas MountainsNile ValleyNile DeltaCataracts of the NileDarfurGulf of AqabaLower EgyptLower NubiaMiddle EgyptNile DeltaNuba MountainsNubiaThe SudansUpper EgyptWestern SaharaMadagascarCentral Highlands (Madagascar)Northern HighlandsRhodesiaNorthSouthThembulandSucculent KarooNama KarooBushveldHighveldFynbosCape Floristic RegionKalahari DesertOkavango DeltaCape PeninsulaFalse BayHydra Bay
Gulf of GuineaBodies of water of BeninBodies of water of CameroonBodies of water of Equatorial GuineaBodies of water of GabonBodies of water of GhanaBodies of water of NigeriaBodies of water of TogoGulfs of AfricaGulfs of the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic OceanCape LopezGabonCape PalmasLiberiaEquatorPrime MeridianlatitudelongitudeNigerVoltaBight of BeninBight of BonnyMaghribSijilmasJenneSão Jorge da MinaElminaGold Coast regionGuineaWest AfricaSouthern AfricaGuineaGuinea-BissauEquatorial GuineaNew GuineaMelanesiaNiger RiverInternational Hydrographic OrganizationSatellite imageryCameroon lineAnnobónEquatorial GuineaBobowasi IslandBiokoislandCoriscoElobey GrandeElobey ChicoSão Tomé and Príncipeisland nationPortugalSão ToméPríncipeGabonextinctvolcanicmountain rangeEquator
Gulf of Guinea
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Gulf of Guinea | |
|---|---|
 Gulf of Guinea map showing the chain of islands formed by the Cameroon line of volcanoes. | |
| Coordinates | 1°0′N 4°0′E / 1.000°N 4.000°E / 1.000; 4.000Coordinates: 1°0′N 4°0′E / 1.000°N 4.000°E / 1.000; 4.000 |
| Native name | Golfe de Guinée |
| River sources | Niger |
| Ocean/sea sources | Atlantic Ocean |
Basin countries | Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, São Tomé and Príncipe, Congo Republic, DR Congo, Angola |
| Surface area | 2,350,000 km2 (910,000 sq mi) |
| Islands | Bioko, São Tomé, Príncipe, Ilhéu Bom Bom, Ilhéu Caroço, Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, Annobon, Corisco, Bobowasi |
 |
| Earth's oceans |
|---|
|
World Ocean |
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean between Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia.[1] The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the gulf.
Among the many rivers that drain into the Gulf of Guinea are the Niger and the Volta. The coastline on the gulf includes the Bight of Benin and the Bight of Bonny.
Contents
1 Name
2 Geography
2.1 Islands in the Gulf of Guinea
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Name
The origin of the name Guinea is thought to be an area in the region, although the specifics are disputed. Bovill (1995) gives a thorough description:[2]
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
The name Guinea is usually said to have been a corrupt form of the name Ghana, picked up by the Portuguese in the Maghrib. The present writer finds this unacceptable. The name Guinea has been in use both in the Maghrib and in Europe long before Prince Henry's time. For example, on a map dated about 1320 by the Genoese cartographer Giovanni di Carignano, who got his information about Africa from a fellow-countryman in Sijilmas [ancient trading city in North Africa], we find Gunuia, and in the Catalan atlas of 1375 as Ginyia. A passage in Leo [Africanus] (vol. III, 822) points to Guinea having been a corrupt form of Jenne [2,000-year-old city in central Mali on Niger river], less famous than Ghana but nevertheless for many centuries famed in the Maghrib as a great market and a seat of learning. The relevant passage reads: "The Kingdom of Ghinea . . . called by the merchants of our nation Gheneoa, by the natural inhabitants thereof Genni and by the Portugals and other people of Europe Ghinea." But it seems more probable that Guinea derives from aguinaou, the Berber for Negro. Marrakech [city in southeastern Morocco] has a gate, built in the twelfth century, called the Bab Aguinaou, the Gate of the Negro (Delafosse, Haut-Sénégal-Niger, II, 277-278). The modern application of the name Guinea to the coast dates only from 1481. In that year the Portuguese built a fort, São Jorge da Mina (modern day Elmina), on the Gold Coast region, and their king, John II, was permitted by the Pope [Sixtus II or Innocent VIII] to style himself Lord of Guinea, a title that survived until the recent extinction of the monarchy.
The name "Guinea" was also applied to south coast of West Africa, north of the Gulf of Guinea, which became known as "Upper Guinea", and the west coast of Southern Africa, to the east, which became known as "Lower Guinea".[citation needed] The name "Guinea" is still attached to the names of three countries in Africa: Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, and Equatorial Guinea, as well as New Guinea in Melanesia.
Geography
The main river shedding its waters in the gulf is the Niger River.
Different definitions of the geographic limits of the Gulf of Guinea are given; the International Hydrographic Organization defines the southwest extent of the Gulf of Guinea as "A line from Cap Lopez (0°37′S 8°43′E / 0.617°S 8.717°E / -0.617; 8.717), in Gabon, northwestward to Ihléu Gago Coutinho (Ilhéu das Rôlas) (0°01′S 6°32′E / 0.017°S 6.533°E / -0.017; 6.533); and thence a line from Ihléu Gago Coutinho northwestward to Cape Palmas (4°22′N 7°44′W / 4.367°N 7.733°W / 4.367; -7.733), in Liberia.[1]
Old French map of the Gulf of Guinea
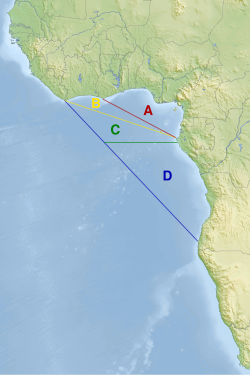
Different limits of the Gulf of Guinea
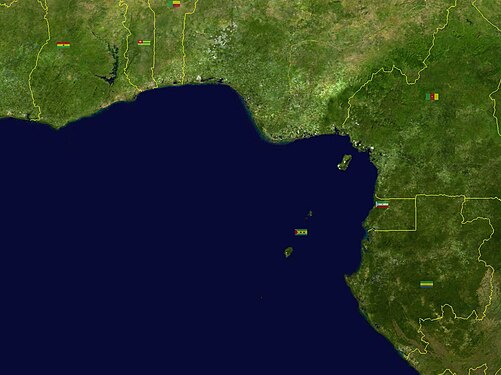
Satellite imagery of the Gulf of Guinea showing borders of states on its shores
Islands in the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea contains a number of islands, the largest of which are in a southwest-northeast chain, forming part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes.
Annobón, also known as Pagalu or Pigalu, is an island that is part of Equatorial Guinea.
Bobowasi Island is an island off the west coast of Africa in the Gulf of Guinea that is part of Western region Ghana.
Bioko is an island off the west coast of Africa in the Gulf of Guinea that is part of Equatorial Guinea.
Corisco is an island belonging to Equatorial Guinea.
Elobey Grande and Elobey Chico are two small islands belonging to Equatorial Guinea.
São Tomé and Príncipe (officially the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe) is a Portuguese-speaking island nation in the Gulf of Guinea that became independent from Portugal in 1975. It is located off the western equatorial coast of Africa and consists of two islands, São Tomé and Príncipe. They are located about 140 kilometres (87 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 kilometres (155 and 140 mi), respectively, off the northwestern coast of Gabon. Both islands are part of an extinct volcanic mountain range. São Tomé, the sizeable southern island, is situated just north of the Equator.
See also
- Benin
- Cameroon
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- Ghana
- Guinea (region)
- Nigeria
- Togo
- Whales in Ghanaian waters
References
^ ab "Limits of Oceans and Seas, Draft 4th Edition: North Atlantic Ocean and its Sub-Divisions". International Hydrographic Organization. 2002. Retrieved 5 April 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Hale, Thomas A. "From the Griot of Roots to the Roots of Griot: A New Look at the Origins of a Controversial African Term for Bard" (PDF). Oral Tradition.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gulf of Guinea. |
- The Gulf of Guinea Commission - CGG - GGC
Categories:
- Gulf of Guinea
- Bodies of water of Benin
- Bodies of water of Cameroon
- Bodies of water of Equatorial Guinea
- Bodies of water of Gabon
- Bodies of water of Ghana
- Bodies of water of Nigeria
- Bodies of water of Togo
- Gulfs of Africa
- Gulfs of the Atlantic Ocean
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||[]).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.572","walltime":"0.792","ppvisitednodes":"value":1793,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":108216,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":8603,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":14,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":4,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":1,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":9131,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":1,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 626.669 1 -total"," 47.99% 300.724 1 Template:Infobox_body_of_water"," 44.65% 279.824 1 Template:Infobox"," 22.76% 142.607 2 Template:Lang"," 21.11% 132.313 1 Template:Native_name"," 11.63% 72.880 1 Template:Reflist"," 10.38% 65.030 2 Template:Cite_web"," 8.88% 55.664 4 Template:Coord"," 6.52% 40.859 1 Template:Citation_needed"," 6.27% 39.291 1 Template:Commons_category"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.303","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":15350909,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1254","timestamp":"20190508114529","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false););"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Gulf of Guinea","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf_of_Guinea","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q41430","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q41430","author":"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects","publisher":"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png","datePublished":"2002-03-02T15:29:07Z","dateModified":"2019-04-18T05:02:13Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a6/Gulf_of_Guinea_%28English%29.jpg","headline":"gulf on the west coast of Africa"(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||[]).push(function()mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":918,"wgHostname":"mw1254"););


